
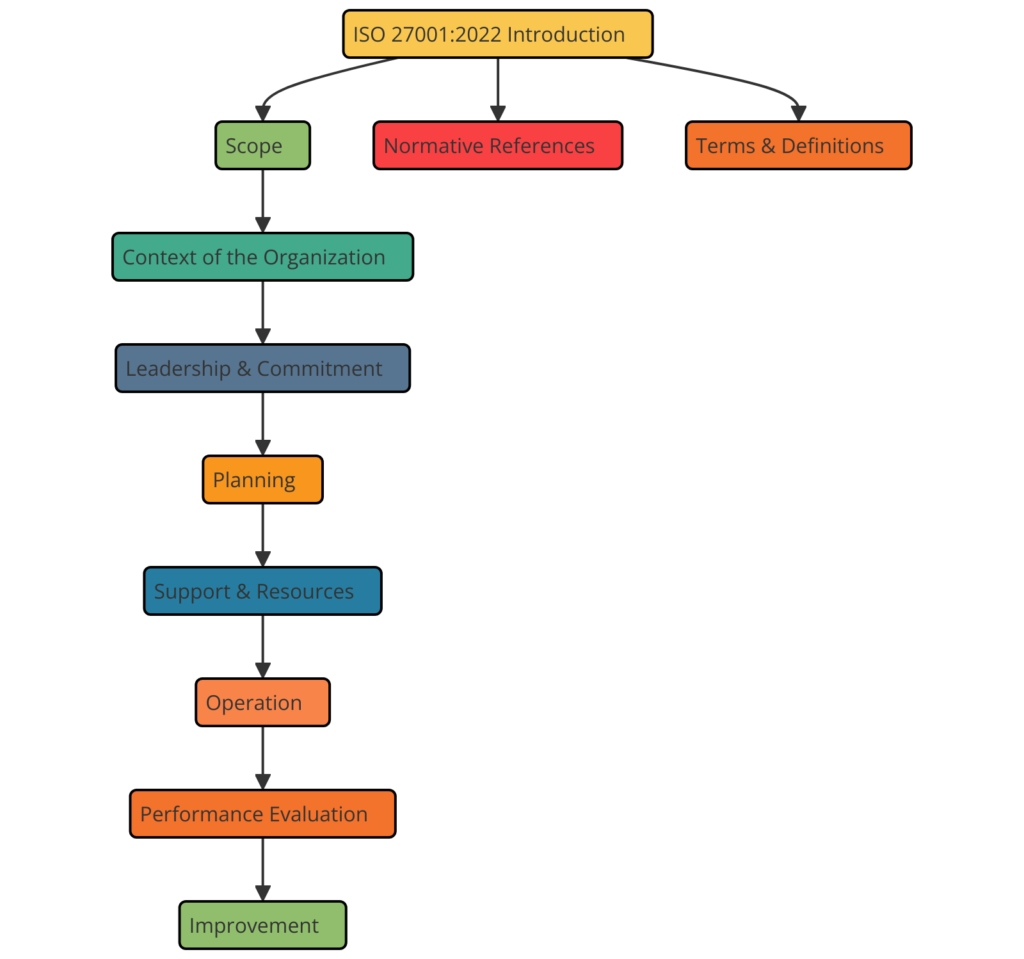
What is ISO 27001:2022?
The ISO 27001:2022 Information Security Management Systems is a globally recognized framework designed to help organizations establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve an Information Security Management System (ISMS). This standard provides a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information, ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and availability. ISO 27001:2022 is the latest version of the international standard for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS).
ISO 27001:2022 is an update to the previous version ISO 27001:2013, reflecting the evolving landscape of information security threats and the increasing importance of cybersecurity and privacy protection.
The standard is suitable for organizations of all sizes and industries, aiming to secure their information assets from a wide range of threats, including cyber-attacks, data breaches, and other security incidents.
What are the Difference Between ISO 27001:2013 vs ISO 27001:2022
The key differences between ISO 27001:2013 and ISO 27001:2022 are:
Emphasis on leadership and top management: ISO 27001:2022 places greater emphasis on the role of top management in establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving the ISMS. The new version requires top management to demonstrate their commitment to information security.
Risk assessment and treatment: ISO 27001:2022 provides more explicit requirements for risk assessment and risk treatment. The new version requires organizations to identify and assess risks based on their likelihood and impact. And to implement appropriate controls to manage those risks.
Performance evaluation: ISO 27001:2022 places greater emphasis on the importance of measuring and evaluating the performance of the ISMS. The new version requires organizations to establish performance metrics and to regularly monitor, measure as well as evaluate the effectiveness of their ISMS.
Integration with business processes: New version provides new guidance on the integration of the ISMS into the organization’s business processes. The new version emphasizes the importance of aligning the ISMS with the organization’s overall strategy and objectives, and of integrating information security considerations into business processes and decision-making.
ISO 27001:2022 provides a more comprehensive and systematic approach to information security management than the previous version. The new version places greater emphasis on leadership and risk management, and provides guidance on integrating the ISMS into the organization’s business processes.
What are the Key Elements of ISO 27001
ISO 27001 provides a framework for managing and protecting an organization’s information assets. The key elements of ISO 27001 include:
- Information Security Management System (ISMS)
- Leadership and Commitment
- Context of the Organization
- Risk Assessment and Treatment
- Information Security Policies
- Information Security Objectives
- Support
- Operation
- Performance Evaluation
- Improvement
- Annex A Controls
Implementing these key elements helps organizations build a robust and resilient information security management system, capable of protecting their information assets from a variety of threats and ensuring compliance with relevant legal and regulatory requirements.
If organization is seeking to achieve ISO 27001:2022 certification, contact us at support@pacificcert.com.
Our team at Pacific Certifications is dedicated to guiding you through the certification process with professionalism and expertise!
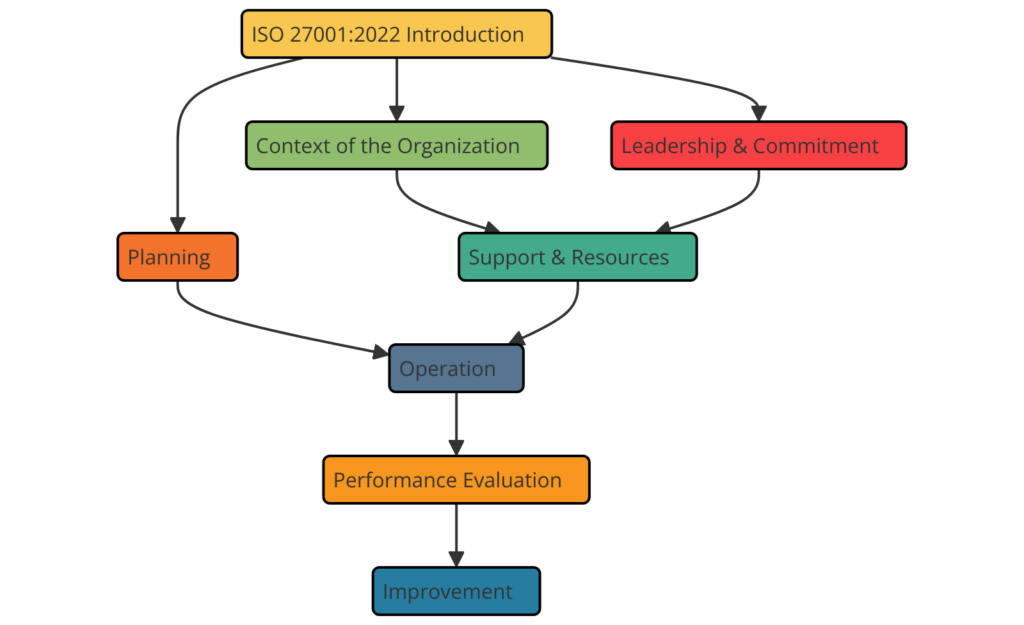
Structure of ISO 27001:2022 – Clause Wise
ISO 27001:2022 is structured into several clauses, each addressing a critical aspect of an Information Security Management System. The clauses provide a framework for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an ISMS.
Here is the clause-wise structure of ISO 27001:
Clause 4: Context of the Organization
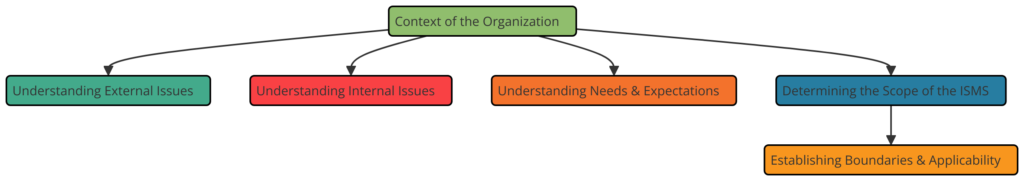
- 4.1 Understanding the Organization and Its Context: Organizations must determine external and internal issues relevant to their purpose and that affect their ability to achieve the intended outcome(s) of the ISMS.
- 4.2 Understanding the Needs and Expectations of Interested Parties: Identifying the requirements of interested parties that are relevant to information security.
- 4.3 Determining the Scope of the ISMS: Establishing the boundaries and applicability of the ISMS.
- 4.4 ISMS: Establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving the ISMS.
Clause 5: Leadership
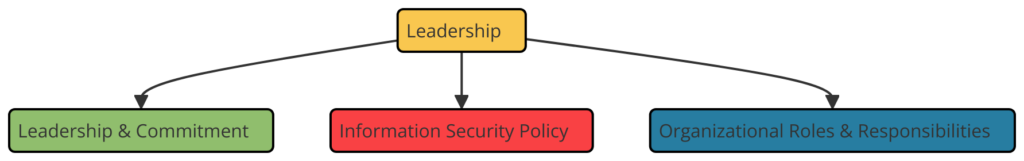
- 5.1 Leadership and Commitment: Top management must demonstrate leadership and commitment to the ISMS.
- 5.2 Information Security Policy: Establishing an information security policy that provides direction and support.
- 5.3 Organizational Roles, Responsibilities, and Authorities: Assigning roles, responsibilities, and authorities for the ISMS.
Clause 6: Planning
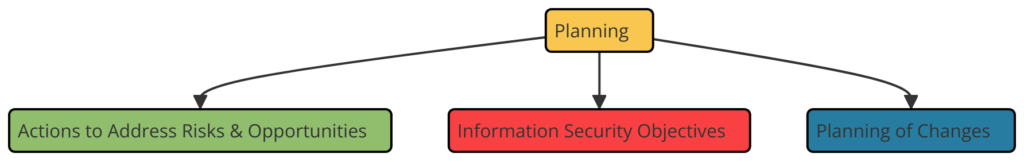
- 6.1 Actions to Address Risks and Opportunities: Identifying and addressing risks and opportunities that can affect the ISMS’s intended outcome.
- 6.1.1 General
- 6.1.2 Information Security Risk Assessment
- 6.1.3 Information Security Risk Treatment
- 6.2 Information Security Objectives and Planning to Achieve Them: Setting measurable information security objectives and planning how to achieve them.
- 6.3 Planning of Changes: Managing changes to the ISMS in a planned manner.
Clause 7: Support
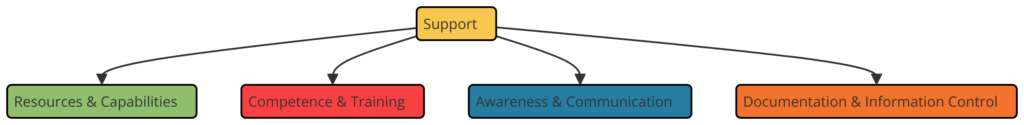
- 7.1 Resources: Determining and providing the resources needed for the ISMS.
- 7.2 Competence: Ensuring personnel are competent on the basis of appropriate education, training, or experience.
- 7.3 Awareness: Ensuring that employees are aware of the information security policy, their contribution to the effectiveness of the ISMS, and the implications of not conforming.
- 7.4 Communication: Determining the internal and external communications relevant to the ISMS.
- 7.5 Documented Information: Creating and updating documented information and ensuring its control.
- 7.5.1 General
- 7.5.2 Creating and Updating
- 7.5.3 Control of Documented Information
Clause 8: Operation
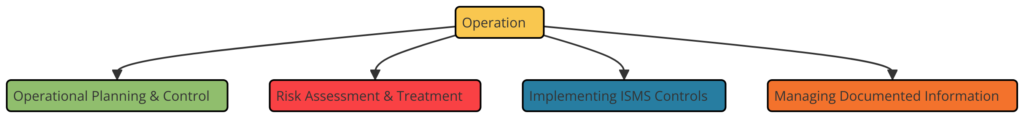
- 8.1 Operational Planning and Control: Planning, implementing, and controlling the processes needed to meet information security requirements and to achieve the objectives.
Clause 9: Performance Evaluation
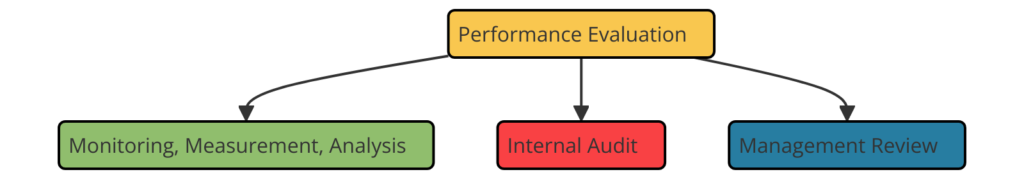
- 9.1 Monitoring, Measurement, Analysis, and Evaluation: Determining what needs to be monitored and measured, and when it shall be performed.
- 9.1.1 General
- 9.1.2 Evaluation of Information Security Performance and Effectiveness
- 9.2 Internal Audit: Conducting internal audits at planned intervals.
- 9.2.1 General
- 9.2.2 Internal Audit Program
- 9.3 Management Review: Conducting management reviews at planned intervals to ensure the ISMS’s continuing suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness.
Clause 10: Improvement
- 10.1 Nonconformity and Corrective Action: Handling nonconformities and taking corrective actions to eliminate the causes of nonconformities.
- 10.2 Continual Improvement: Continually improving the suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness of the ISMS.
Annex A: Reference Control Objectives and Controls
Annex A provides a list of controls that can be selected as part of the risk treatment process. These controls are organized into various categories such as organizational controls, people controls, physical controls, and technological controls. They align with the information security requirements and help in implementing a robust ISMS.
This structure helps organizations systematically address all aspects of information security management, ensuring a comprehensive and effective approach to protecting their information assets.
Looking to get ISO 27001:2022 certified? Reach out to us at support@pacificcert.com!
We’re here to help you every step of the way and make the process as smooth as possible.
Audit Checklist for ISO 27001:2022: Clause-wise

When you are creating a detailed audit checklist for ISO 27001, you should ensure that all aspects of the Information Security Management System (ISMS) are thoroughly reviewed and compliant with the standard’s requirements. Below is a clause-wise audit checklist for ISO 27001:2022:
Clause 4: Context of the Organization
- Has the organization determined external and internal issues relevant to its purpose and affecting its ISMS?
- Are these issues documented and reviewed regularly?
- Has the organization identified interested parties relevant to the ISMS?
- Are their requirements documented and understood?
- Is the scope of the ISMS clearly defined, documented, and available?
- Does it consider external and internal issues, requirements of interested parties, and interfaces and dependencies with other organizations?
- Is the ISMS established, implemented, maintained, and continually improved in accordance with the standard?
Clause 5: Leadership
- Does top management demonstrate leadership and commitment to the ISMS?
- Are there records of their involvement and support?
- Is there an established information security policy?
- Is the policy appropriate, communicated, and understood within the organization?
- Are roles and responsibilities for information security clearly defined and communicated?
- Are authorities for ISMS roles assigned and documented?
Clause 6: Planning
- Are processes established to address risks and opportunities?
- Is there a documented risk assessment process?
- Are information security risks identified, assessed, and documented?
- Is there a documented risk treatment plan?
- Are risk treatment options identified and implemented?
- Are information security objectives established, documented, and aligned with the information security policy?
- Are plans in place to achieve these objectives?
- Are changes to the ISMS planned, documented, and reviewed for their impact on information security?
Clause 7: Support
- Are resources determined and provided for the establishment, implementation, maintenance, and continual improvement of the ISMS?
- Is competence determined and ensured for personnel affecting information security performance?
- Are training and awareness programs documented and effective?
- Are personnel aware of the information security policy, their contribution to the effectiveness of the ISMS, and implications of not conforming?
- Are internal and external communication processes established and documented?
- Are relevant communications about information security timely and effective?
- Is documented information required by the ISMS and the standard established and controlled?
- Is documented information created, updated, and appropriately identified?
- Is documented information controlled to ensure its adequacy, suitability, and availability?
Clause 8: Operation
- Are processes needed to meet information security requirements planned, implemented, and controlled?
- Are changes managed, and are outsourced processes controlled?
Clause 9: Performance Evaluation
- Are methods for monitoring, measurement, analysis, and evaluation established and documented?
- Is the performance and effectiveness of the ISMS evaluated regularly?
- Are internal audits conducted at planned intervals?
- Is there an established internal audit program?
- Are audit results documented and corrective actions taken?
- Are management reviews conducted at planned intervals?
- Are inputs and outputs of the management review documented and actions taken?
Clause 10: Improvement
- Are nonconformities identified and corrective actions taken?
- Are actions documented, reviewed, and their effectiveness evaluated?
- Is there a process for continual improvement of the ISMS?
- Are improvements identified, implemented, and documented?
Annex A: Reference Control Objectives and Controls
- Are the controls from Annex A selected based on the risk treatment plan?
- Are selected controls implemented, maintained, and their effectiveness reviewed?
- Is there documented evidence of control implementation and reviews?
This checklist provides a structured approach to auditing an ISMS against ISO 27001:2022, ensuring all clauses and their requirements are systematically reviewed and compliant.
Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) Explained: ISO 27001:2022
The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle is a systematic series of steps for continuous improvement and management of processes. ISO 27001:2022, which provides a framework for an Information Security Management System, integrates the PDCA model to ensure that information security processes are effectively managed and continuously improved, see in the graph how it can be implemented:
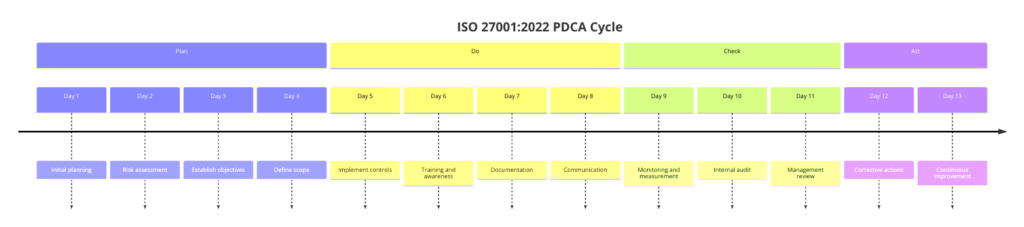
Here’s an explanation of each phase of the PDCA cycle in the context of ISO 27001:
Plan
Context of the Organization (Clause 4):
- Understanding internal and external issues affecting information security.
- Identifying the needs and expectations of interested parties.
- Determining the scope of the ISMS.
- Establishing the ISMS.
Leadership (Clause 5):
- Securing top management commitment and support for the ISMS.
- Establishing an information security policy.
- Defining roles, responsibilities, and authorities.
Planning (Clause 6):
- Identifying information security risks and opportunities.
- Conducting risk assessments.
- Developing a risk treatment plan.
- Setting information security objectives and planning how to achieve them.
Support (Clause 7):
- Allocating resources.
- Ensuring personnel competence.
- Raising awareness and ensuring effective communication.
- Maintaining and controlling documented information.
Do
Operational Planning and Control (Clause 8):
- Implementing risk treatment plans.
- Managing operations to meet information security objectives.
- Controlling outsourced processes that impact information security.
Implementation of Controls (Annex A):
- Selecting and applying appropriate controls from Annex A based on the risk assessment and treatment plan.
Check
Performance Evaluation (Clause 9):
Monitoring and Measurement:
- Regularly monitoring and measuring the ISMS’s performance and effectiveness.
Internal Audit:
- Conducting internal audits to assess the ISMS against the ISO 27001 requirements and the organization’s own criteria.
Management Review:
- Reviewing the ISMS at planned intervals to ensure its continuing suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness.
Evaluation of Controls (Annex A):
- Reviewing and evaluating the effectiveness of implemented controls to ensure they address identified risks.
Act
Improvement (Clause 10):
Nonconformity and Corrective Action:
- Identifying and addressing nonconformities.
- Taking corrective actions to eliminate the causes of nonconformities.
Continual Improvement:
- Continuously improving the ISMS’s suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness.
- Adapting to changes in risks, regulatory requirements, and organizational needs.
The PDCA cycle ensures that an organization systematically plans, implements, monitors, and continually improves its ISMS. The PDCA model promotes a proactive approach to information security, ensuring that the ISMS evolves in response to changing threats and business needs.
Take your business to the next level with ISO 27001:2022 certification! Contact us at support@pacificcert.com to learn how we can help you achieve this prestigious standard and enhance your information security management!
Global Trends in ISO 27001 Adoption and Benefits for Companies
ISO 27001 continues to be a critical standard for organizations worldwide, helping them manage and protect their information assets. The adoption of ISO 27001 is growing, driven by increasing cybersecurity threats, regulatory requirements, and the need for organizations to build trust with their stakeholders, the graph below shows yearly growth from 2017 to 2024:
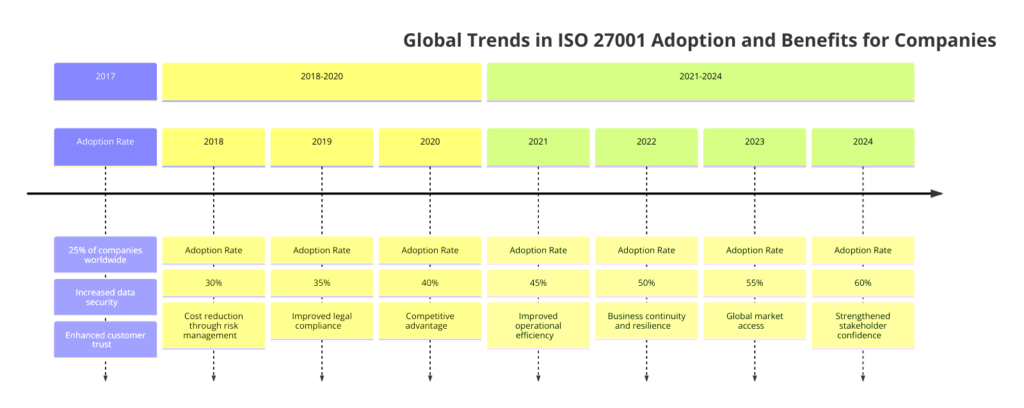
Global Trends
- The adoption of ISO 27001 is expanding across various sectors, particularly in industries where data security is paramount, such as healthcare, finance, and IT services. Companies in these sectors are increasingly recognizing the need to protect sensitive information and ensure business continuity.
- Organizations are integrating ISO 27001 with other cybersecurity and privacy frameworks to create a comprehensive approach to information security. This trend is partly driven by regulations like GDPR in Europe, which mandate stringent data protection measures.
- With the shift towards cloud computing, ISO 27001 has become essential for organizations to manage cloud-related security risks. The latest updates to the standard, such as those in ISO 27001:2022, reflect this by including controls specifically aimed at cloud security and other emerging technologies (NQA).
For more detailed insights and case studies on the benefits of ISO 27001, you can refer to these resources from:
PCG
CANVA
Mint Security
Workpole Partnership
ISO 27001 Certification Requirements: Implementing ISO 27001:2022
For Implementing ISO 27001:2022 organizations must meet to establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve an Information Security Management System (ISMS). The following outlines the key requirements and steps for implementing ISO 27001:2022:

- Understand the Standard
- Define the Scope of the ISMS
- Conduct a Risk Assessment
- Establish Information Security Policies and Objectives
- Implement Necessary Controls (Annex A)
- Develop and Maintain Documented Information
- Conduct Training and Awareness Programs
- Monitor and Review the ISMS
- Continual Improvement
Implementing ISO 27001:2022 requires a structured approach and a commitment to continuous improvement. By meeting these requirements, organizations can effectively manage their information security risks and enhance their overall security posture.
Steps to achieve ISO 27001:2022 to Certification
Achieving ISO 27001:2022 certification involves a structured approach that ensures an organization has a robust Information Security Management System (ISMS) in place. Here are the steps to achieve ISO 27001:2022 certification:
Understanding ISO 27001:2022: Obtain a copy of ISO 27001:2022 and understand its requirements, including the main clauses and Annex A controls. Ensure that key personnel understand the standard’s requirements and the benefits of certification.
Obtain Top Management Support: Secure commitment from top management to provide the necessary resources and support for the ISMS implementation.
Define the Scope of the ISMS: Determine the boundaries and applicability of the ISMS based on the organization’s context and the needs of interested parties.
Conduct a Gap Analysis: Initial Assessment: Perform a gap analysis to identify areas that need improvement to meet ISO 27001 requirements. This involves reviewing existing security measures and identifying gaps against the standard’s requirements.
Develop an ISMS
- Policies and Procedures: Develop and document information security policies, procedures, and controls based on the identified gaps and the requirements of ISO 27001.
- Risk Assessment: Identify and evaluate information security risks. Develop a risk treatment plan to address these risks.
Implement the ISMS
- Implementation: Implement the documented policies, procedures, and controls across the organization.
- Training and Awareness: Conduct training sessions to ensure that all employees understand their roles and responsibilities within the ISMS.
Internal Audit and Management Review
- Internal Audit: Conduct an internal audit to evaluate the effectiveness of the ISMS and identify any nonconformities.
- Management Review: Conduct a management review to assess the ISMS’s performance and make necessary adjustments.
Stage 1 Audit (Documentation Review)- Certification body
- Documentation Audit: An external auditor from the selected certification body reviews the ISMS documentation to ensure it meets the requirements of ISO 27001. This stage verifies that all necessary documents are in place and correctly implemented.
Stage 2 Audit (Implementation Review)
- The auditor assesses the actual implementation of the ISMS. This involves verifying that the policies, procedures, and controls are effectively applied and that the ISMS is functioning as intended.
- The auditor will collect evidence through interviews, observations, and reviews of records to confirm compliance with ISO 27001.
Certification Decision
- Certification Issuance
- Corrective Actions: If there are nonconformities, corrective actions must be taken and verified by the auditor before certification can be granted.
Post-Certification Activities
- Surveillance Audits: Regular surveillance audits are conducted (typically annually) to ensure continued compliance and effectiveness of the ISMS.
- Continually improve the ISMS based on audit findings, changes in the organizational environment, and evolving security threats.
By following these steps, organizations can systematically implement an effective ISMS and achieve ISO 27001:2022 certification, enhancing their information security posture and gaining various business benefits.
What are the Benefits of ISO 27001
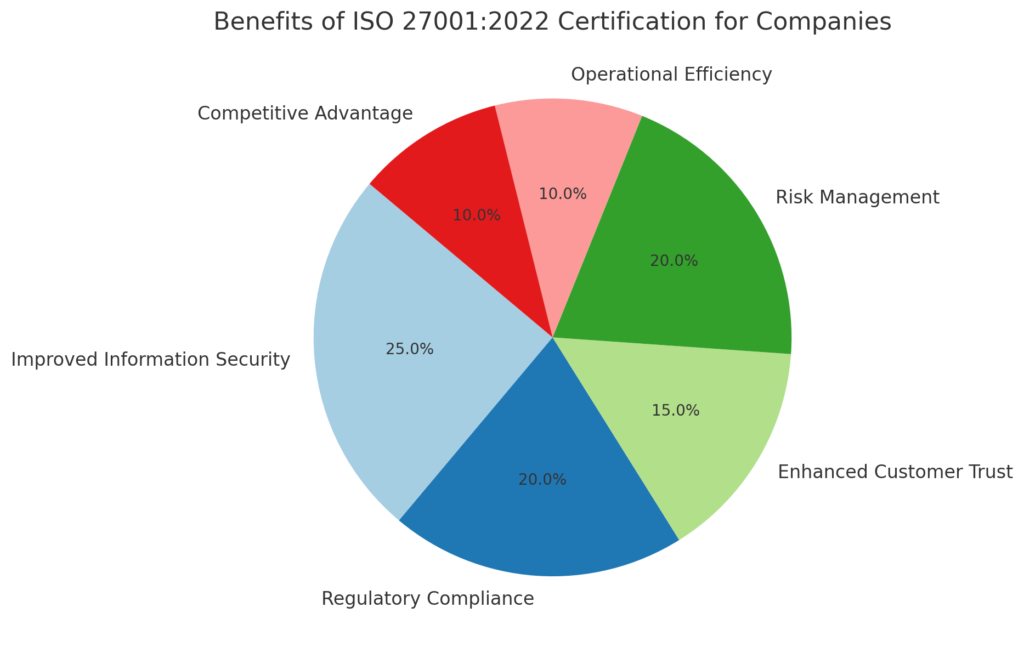
Enhanced Data Security: ISO 27001 provides a robust framework for managing information security risks, protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber-attacks.
Regulatory Compliance: Helps organizations comply with various legal, regulatory, and contractual requirements, such as GDPR, reducing the risk of legal fines
Systematically identifies, assesses, and manages information security risks, leading to more effective risk mitigation.
Demonstrates a commitment to information security, enhancing trust and credibility with customers, partners, and stakeholders.
Differentiates the organization from competitors, making it more attractive to customers and partners who prioritize security.
Operational Efficiency: Streamlines processes and improves decision-making related to information security, leading to operational efficiencies and cost savings.
Provides assurance to customers that their data is managed securely, fostering customer loyalty and improving business relationships.
Business Continuity: Enhances the organization’s ability to manage and recover from information security incidents, ensuring business continuity.
Need ISO 27001:2022 certification? Email us at support@pacificcert.com today! We’ll help you get certified quickly and efficiently.
What are the ISO 27001:2022 Control Points
ISO 27001:2022 includes a total of 114 control points across 14 categories, known as Annex A. These controls address specific information security risks and provide guidance on implementing appropriate controls to manage those risks. Therefore, The categories and the number of control points in each category are:
- Information Security Policies (2 controls)
- Organization of Information Security (13 controls)
- Human Resource Security (8 controls)
- Asset Management (10 controls)
- Access Control (14 controls)
- Cryptography (3 controls)
- Physical and Environmental Security (16 controls)
- Operations Security (13 controls)
- Communications Security (10 controls)
- System Acquisition, Development, and Maintenance (17 controls)
- Supplier Relationships (6 controls)
- Information Security Incident Management (8 controls)
- Information Security Aspects of Business Continuity Management (4 controls)
- Compliance (10 controls)
How ISO Certifications can help to reduce the risks of Cyber attacks on critical Infrastructure?
The implementation of ISO certifications, particularly ISO 27001, can significantly contribute to reducing the risks of cyber attacks on critical infrastructure. ISO 27001 is one of the most popular ISO standard for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) that provides a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information and ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Below are some key ways in which ISO certifications can help mitigate cyber risks:
Risk Assessment and Management
- Identification of Vulnerabilities: ISO 27001 mandates organizations to conduct regular risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities in their systems. This proactive approach helps in early detection of potential threats.
- Evidence: A study by the Ponemon Institute found that organizations with a robust risk assessment process experienced fewer data breaches.
- Risk Treatment Plans: Once risks are identified, ISO 27001 requires the formulation of risk treatment plans. These plans outline the controls and measures to mitigate identified risks.
- Evidence: According to a report by Verizon, 76% of breaches were financially motivated, and a risk treatment plan can help in prioritizing risks based on their potential financial impact.
Implementation of Controls
- Access Control: ISO 27001 emphasizes the importance of implementing access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to critical infrastructure.
- Evidence: The 2020 IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report indicated that 19% of all breaches were caused by unauthorized access.
- Encryption and Data Protection: The standard recommends encryption and other data protection methods to safeguard sensitive information.Evidence: According to the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), encryption is a key factor in reducing the impact of data breaches.
Regular Audits and Monitoring
- Continuous Monitoring: ISO 27001 requires continuous monitoring of the ISMS to ensure its effectiveness and to detect any anomalies that could indicate a cyber threat.Evidence: A study by the SANS Institute found that continuous monitoring could reduce the time to detect cyber incidents by up to 86%.
- Third-Party Audits: Being ISO certified means undergoing regular third-party audits, which provide an unbiased review of the organization’s security posture.Evidence: According to ISACA, third-party audits are crucial for ensuring that security controls are both effective and up-to-date.
Employee Training and Awareness
- Security Training: ISO 27001 insists on regular training and awareness programs for employees, as human error is a significant factor in security breaches.
- Evidence: Cybersecurity firm CybSafe found that human error accounted for 90% of data breaches in 2019.
Incident Response Plan
- Preparedness: ISO 27001 requires organizations to have an incident response plan in place, which can be invaluable in the event of a cyberattack.
- Evidence: According to a report by Deloitte, organizations with an incident response plan experienced less severe financial losses during a cyber incident.
In conclusion, Pacific Certifications, by offering ISO 27001 and other relevant certifications, plays a pivotal role in enhancing the cybersecurity posture of organizations, thereby reducing the risks associated with cyberattacks on critical infrastructure. The structured approach provided by these certifications ensures that organizations are better equipped to identify, manage, and mitigate cyber risks effectively.
Pacific Certifications is accredited by ABIS, you need more support with ISO 27001:2022 please contact us at +91-8595603096 or support@pacificcert.com.
Read About: ISO 2782 RUBBER









